Abstract
Background/Objective: Breakthrough hemolysis (BTH) is the return of hemolytic disease activity during treatment with complement C5 inhibitors for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). BTH may be associated with inadequate C5 inhibition or complement activating conditions (eg, infection). Despite reports that up to 19% of patients (pts) receiving eculizumab may experience BTH, there is no commonly accepted definition of BTH. The definition of BTH was derived from literature review and expert consensus. BTH was defined as ≥1 new or worsening symptom/sign of intravascular hemolysis (fatigue, hemoglobinuria, abdominal pain, dyspnea, anemia [hemoglobin <10 g/dL], major adverse vascular event [including thrombosis], dysphagia, or erectile dysfunction) in the presence of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) ≥2 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). In the 2 largest pivotal studies in PNH pts to date, ravulizumab q8w was statistically significantly noninferior to eculizumab 900 mg q2w, with point estimates favoring ravulizumab for all primary (LDH normalization, transfusion avoidance [study 301], percent change in LDH [study 302]) and key secondary endpoints (including BTH). Ravulizumab reduced free C5 levels to <0.5 μg/mL in all pts at all times; eculizumab did not consistently achieve this level of complement inhibition, providing a mechanistic basis for consistency of the point estimates for all endpoints. In study 301, LDH levels had to be decreased to <1.5 xULN prior to a BTH episode. Here we report BTH prevalence and causality using a common definition in the setting of 2 well-controlled clinical studies.
Methods: Two phase 3, randomized, open-label, noninferiority, multicenter studies (study 301, NCT02946463; study 302, NCT03056040) included pts ≥18 years of age with confirmed PNH diagnoses. Pts in study 301 were naive to C5 inhibitor therapy, with LDH ≥1.5 xULN and ≥1 sign/symptom of PNH at screening. Pts in study 302 were stable on eculizumab treatment for ≥6 months, with LDH ≤1.5 xULN at screening. Pts received weight-based dosing of ravulizumab q8w or the approved eculizumab dose (900 mg q2w) for 183 days. Higher eculizumab doses were prohibited.
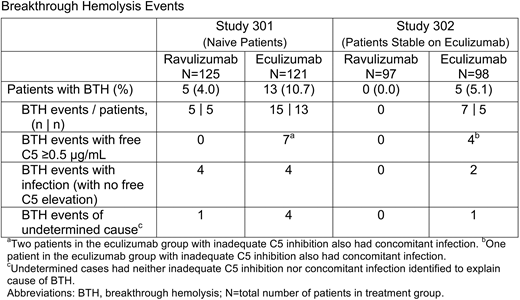
Results: In study 301, 246 pts received ravulizumab (n=125) or eculizumab (n=121); in study 302, 195 pts received ravulizumab (n=97) or eculizumab (n=98). Ravulizumab was associated with fewer episodes of BTH than eculizumab in both studies. In study 301, 5 pts (4.0%) experienced BTH in the ravulizumab group vs 13 pts (10.7%) in the eculizumab group; between-group difference (95% confidence interval [CI]) was −6.7% (−14.21%, 0.18%; P=0.0558 for superiority). In the eculizumab group, 7/15 events were temporally associated with elevations in free C5 (C5 ≥0.5 μg/mL), suggesting inadequate C5 inhibition. No BTH events in the ravulizumab group were associated with inadequate C5 inhibition. Among the BTH events in the ravulizumab group, the majority, 4/5 events, were associated with infection. In the eculizumab group, infection was associated with 6/15 BTH events, including 2 infections in pts with inadequate C5 inhibition. In study 302, no pts in the ravulizumab group experienced BTH vs 5 pts (5.1%) in the eculizumab group (1 pt had 3 BTH events, requiring hospitalization and study discontinuation for lack of efficacy); the between-group difference (95% CI) was −5.1% (−18.99%, 8.89%). Four of 7 BTH events in the eculizumab group were associated with concomitant elevations in free C5. Infection was associated with 3/7 BTH events, including 1 infection in a pt with inadequate C5 inhibition (Table). There was no clear pattern for timing of BTH events. All BTH episodes in the eculizumab groups were reported at the q2w study visits associated with pharmacokinetic (PK) troughs. All BTH episodes in the ravulizumab groups were reported at the q2w study visits, but not necessarily at q8w PK troughs.
Conclusions: No BTH events in the ravulizumab group were associated with elevations in free C5. In contrast, pts treated with eculizumab 900 mg q2w experienced multiple BTH events with elevations in free C5 suggesting suboptimal C5 control. Similar numbers of pts receiving ravulizumab or eculizumab experienced infection-related BTH, possibly due to proximal complement activation. Differences in BTH rates for ravulizumab vs eculizumab may be due to improved pharmacodynamics (C5 inhibition throughout the dosing interval) and the optimized ravulizumab dosing regimen.
Peffault De Latour:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen Inc.: Research Funding. Rottinghaus:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Röth:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bioverativ: Consultancy, Honoraria. Risitano:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Amyndas Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Pfizer Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Weitz:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria. Hillmen:Novartis: Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Acerta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding. Maciejewski:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Consultancy; Apellis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Apellis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Consultancy. Szer:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support , Research Funding. Lee:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Kulasekararaj:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Support . Volles:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Damokosh:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Ortiz:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Shafner:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Hill:Bioverativ: Consultancy, Honoraria; Akari: Consultancy, Honoraria; Ra Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Regeneron: Consultancy, Honoraria; Apellis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria. Schrezenmeier:Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal